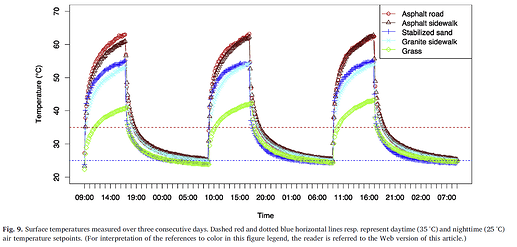
Well, I was investigating a little more about my question number 1, and I show my conclusions, I appreciate if someone can check these ideas, if they find something wrong.
I found the most important values to change the surface temperature and air temperature from radiation of the surface material (Oh surprise) I didnt use to change this parameters before for normal energy indoor simulations.
Attach link to description of each surface properties: https://designbuilder.co.uk/helpv4.2/Content/SurfaceProperties.htm
As energyplus has surfaces properties by default, I attach some materials properties:
Solar absortance: https://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/solar-radiation-absorbed-materials-d_1568.html
Thermal absortance (aka emissitivy coefficients): https://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/emissivity-coefficients-d_447.html
If I create these materials:
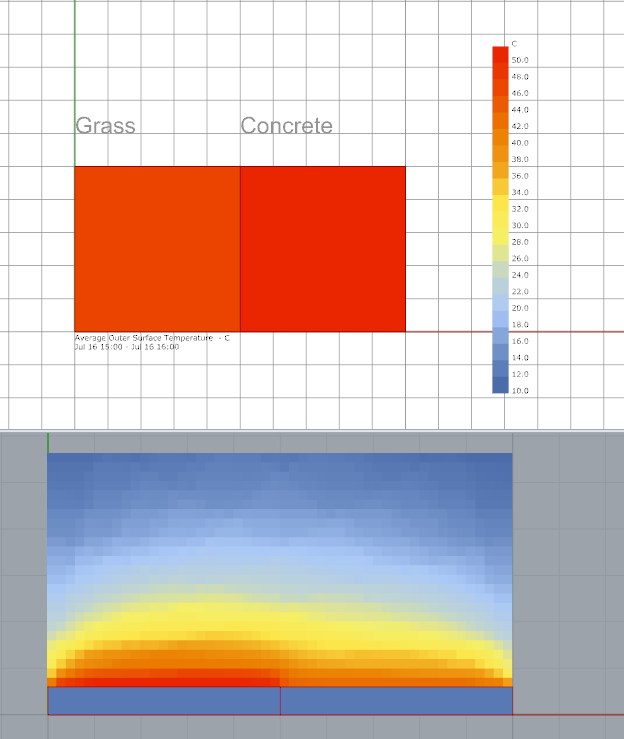
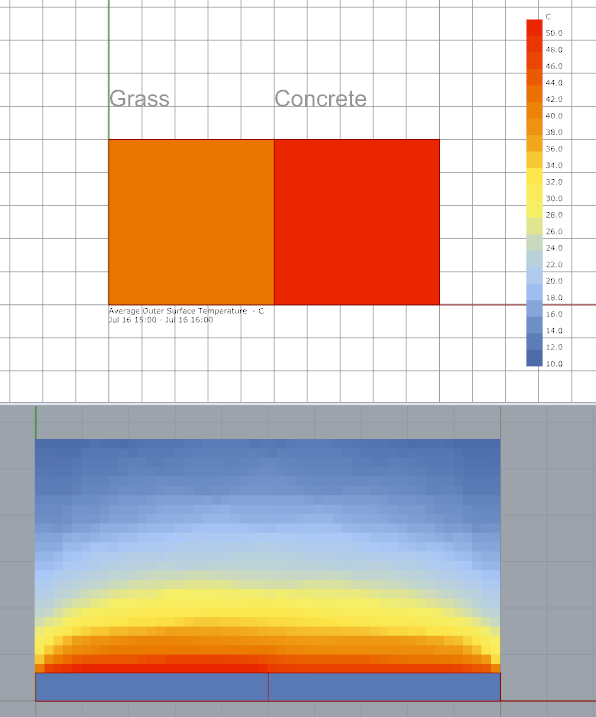
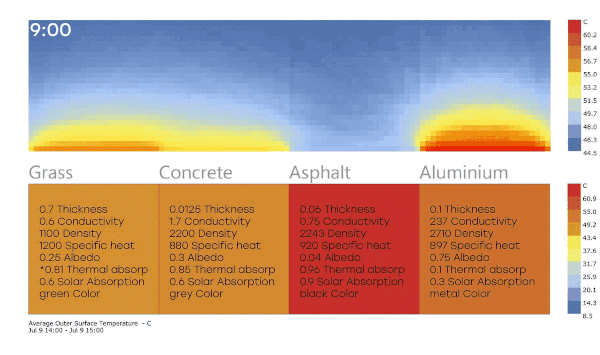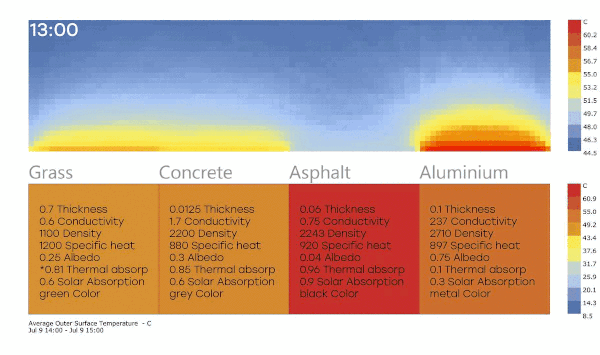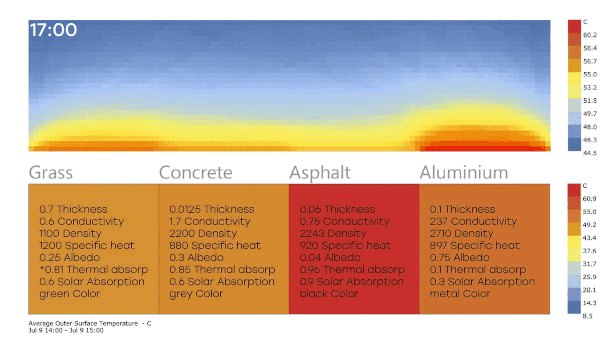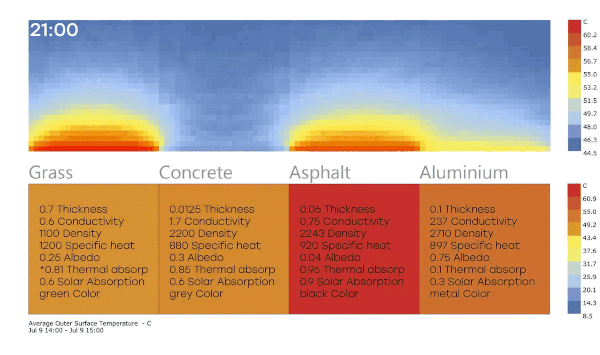
Grasss
Thermal absorptance (0.81 - Because energyplus battery doesnt allow setting low 0.6 for grass material)
Solar absorptance 0.6
Concrete
Thermal absorptance 0.85
Solar absorptance 0.60
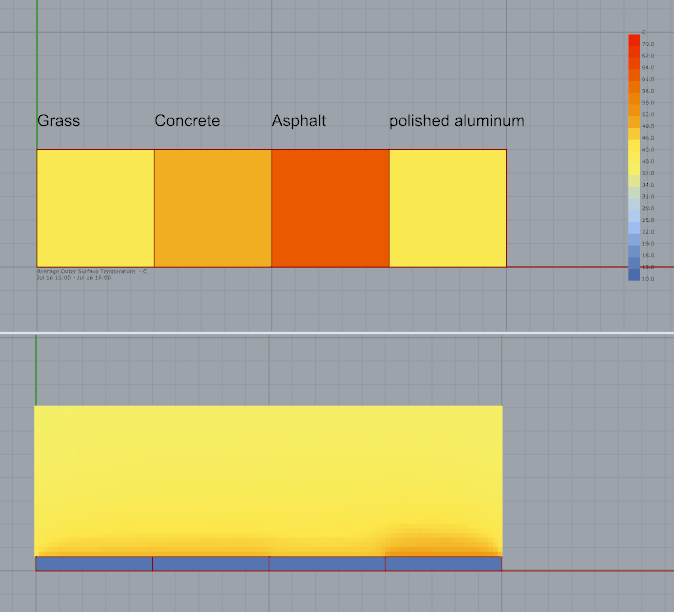
Asphalt
Thermal absorptance 0.96
Solar absorptance 0.90
Polished metal
Thermal absorptance 0.10
Solar absorptance 0.30
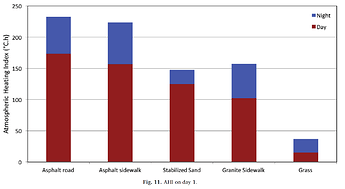
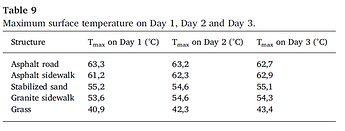
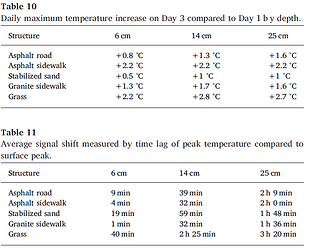
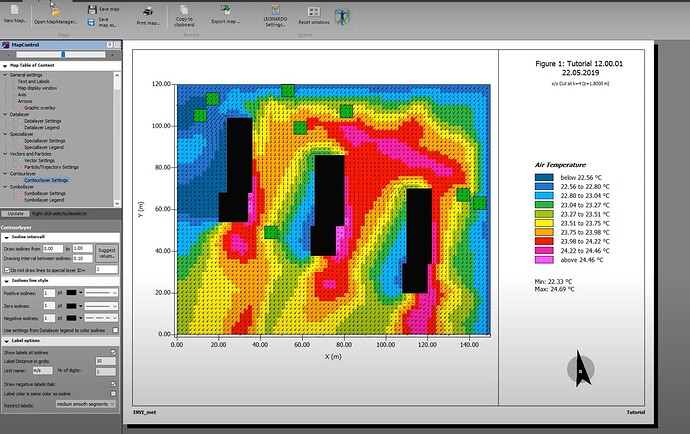
I have these results (The air temperature surfaces analysis is PET (physchological equivalent temperature)
I see the surface of asphalt is the warmest material (Because has high thermal and solar absortance), and the polsihed metal is less warm (Has low values). but I was surprised because the radiant temperature is higher in the metal.
So can I say the low solar and thermal absortance materials increase the heat island effect? I though high absortance materials like asphalt has more impact.
Also, I think these result are not very reliable, because the surfaces are really little, If I set the air temperature I didnt see big changes.
The rest of the doubs, I didnt found any answer.
Thanks.